In an era of escalating healthcare costs and ever-changing insurance landscapes, Americans are increasingly turning to Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) as a powerful tool to take control of their medical expenses.
The IRS recently released guidance providing the 2024 inflation-adjusted amounts for Health Savings Accounts (HSAs). This year’s high inflation rates will result in next year’s amounts being the largest increase yet.
HSA basics
HSAs, a tax-advantaged savings vehicle, offer individuals a unique opportunity to save for current and future healthcare needs while reaping substantial financial benefits. These accounts, often coupled with high-deductible health plans, enable individuals to set aside pre-tax dollars that can be utilized for qualified medical expenses, ranging from doctor visits and prescriptions to dental care and medical procedures.
With their flexible nature and potential for long-term growth, HSAs have emerged as a popular choice for savvy consumers seeking greater financial security and a means to navigate the complex healthcare landscape.
Inflation adjustments for 2024
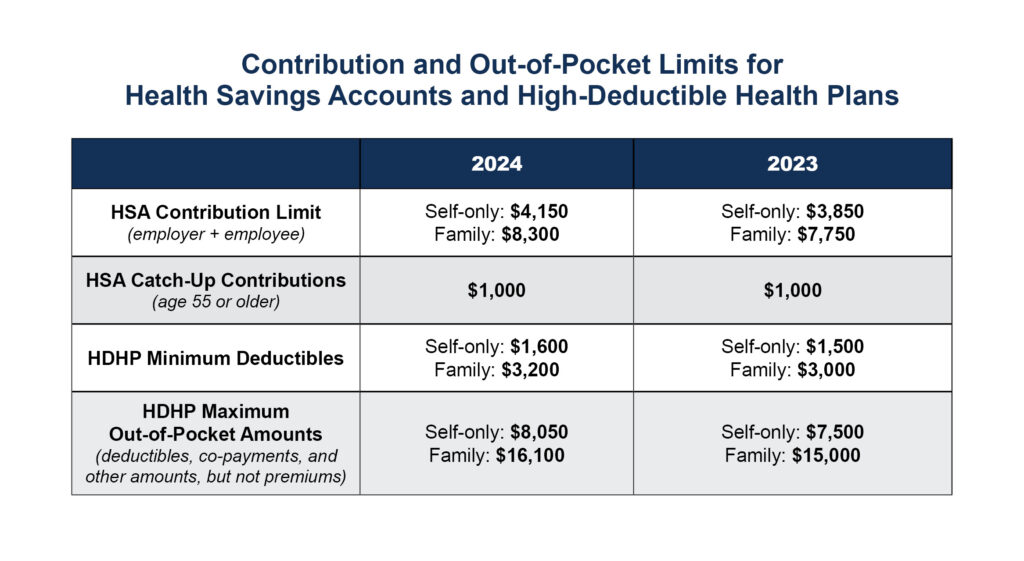
In Revenue Procedure 2023-23, the IRS announced the annual limit on HSA contributions for self-only coverage will be $4,150, a 7.8% increase from the $3,850 limit in 2023. For family coverage, the HSA contribution limit jumps to $8,300, up 7.1% from $7,750 in 2023.
Additionally, participants 55 and older can contribute an extra $1,000 to their HSAs. This amount will remain unchanged.
Starting in 2024, a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) must have a deductible of at least $1,600 for self-only coverage, up from $1,500 in 2023, or $3,200 for family coverage, up from $3,000, the IRS noted. Annual out-of-pocket expense maximums (deductibles, co-payments and other amounts, but not premiums) cannot exceed $8,050 for self-only coverage in 2024 (up from $7,500 in 2023) or $16,100 for family coverage (up from $15,000).
The IRS also announced it will raise the maximum amount that employers may contribute to an excepted-benefit health reimbursement arrangement (HRA) in 2024 to $2,100—up from the 2023 amount of $1,950.
Reap the rewards
As healthcare costs continue to soar, HSAs provide individuals with a dual advantage of tax savings and greater control over their healthcare spending. Contributions to HSAs are tax-deductible, meaning individuals can reduce their taxable income while building up a dedicated fund to cover future medical expenses. Moreover, the interest and investment gains earned within an HSA are tax-free, allowing individuals to grow their savings over time. This combination of tax benefits, compounded with potential investment growth, positions HSAs as a compelling long-term savings strategy that can supplement retirement planning.

